Service Portfolio
Filter
Informing & Planning · Publishing & Archiving · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
Betty's (Re) Search Engine aims to solve the issue of finding research software. The engine searches for software repositories that match a given search string and then tries to find corresponding publications as well as all available metadata. This enables users to sort the repositories based on the number of citations, apply various filters and it also directly provides an impression about the research contexts in which a software has been successfully applied.
Informing & Planning · Organising & Processing · Storing & Computing · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
Coscine is a RDM platform for the active phase of research projects that enables NFDI4ING researchers to access storage space on DataStorage.nrw while guaranteeing the FAIR principles. Projects created in Coscine enable role management, metadata management, public sharing of data, referencing with PIDs and archiving of research and metadata for 10 years. In addition, project-related GitLab repositories can be integrated and external files linked. Registration takes place via your own organization (using the NFDI4ING community AAI) or ORCiD.
Informing & Planning · Publishing & Archiving · Finding & Re-Using
The Data Collections Explorer is an information system for the engineering community. It facilitates sharing of and searching for discipline specific repositories, archives, and databases, as well as for datasets published individually by research groups. Scientists can get a quick overview of the most important facts about services and datasets, such as access rights or usage restrictions. A SPARQL endpoint ensures programmatic access for integration with third-party services.
Informing & Planning · Organising & Processing · Describing & Documenting · Learning & Teaching
"Data Quality Metrics Webpage" is a knowledge platform offering in-depth resources on data quality, FAIR principles, and image and machine learning metrics. Built on ReadTheDocs with GitHub, it supports decentralized editing and easy updates using reStructuredText, requiring no specialized software. The platform provides, practical guidance with examples, images, and code snippets, making it accessible to users for applying data concepts, optimizing models, and enhancing understanding.
Storing & Computing
The data transfer federation aims to increase mobility of data by providing a low-level service that allows asynchronous bulk transfer of large quantities of files from one storage cluster to another.
Publishing & Archiving · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
DataDesc is a framework that allows describing data models of software interfaces with machine-actionable metadata. The framework provides a specialized metadata schema, an exchange format and support tools for the easy collection and automated publishing of software documentation. DataDesc practically increases the FAIRness, i.e., findability, accessibility, interoperability, and the reusability of research software, as well as effectively promotes its impact on research.
Publishing & Archiving · Storing & Computing · Finding & Re-Using
The Field Database Platform (FDP) prioritizes the accessibility and reusability of data, allowing researchers to interact with field datasets more effectively. By providing tools for data exploration and previewing based on operational and environmental parameters, FDP ensures users are guided in finding relevant datasets, avoiding irrelevant or redundant information. This platform enhances data reusability and promotes FAIR principles, significantly improving the research experience compared to traditional data platforms.
Organising & Processing · Publishing & Archiving · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
A python-written metadata crawler that allows to automatically retrieve relevant research metadata from script-based workflows on HPC systems. The tool offers a flexible approach to metadata collection, as the metadata scheme can be read out from an ontology file. Through minimal user input, the crawler can be adapted to the user’s needs and easily implemented within the workflow, enabling to retrieve relevant metadata.
Publishing & Archiving · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
The NFDI4Ing Data Ingest Service is the gateway for enhanced research data publication in architecture and civil engineering. With flexible metadata profiles and automation processes, ing.est visualizes your 3D data, assigns persistent identifiers, and ensures long-term archiving with ease.
Informing & Planning · Publishing & Archiving · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using · Learning & Teaching
Ing.grid is a scholarly-led diamond open access journal for FAIR data management in engineering sciences. It uses an open peer review process and accepts data and software submissions in addition to regular manuscripts.
Informing & Planning · Organising & Processing · Describing & Documenting
Jarves provides guidance in RDM by ordering the RDM activities based on their occurrence in the engineering research process. Taking into account the specific RDM requirements of a research project, e.g. requirements of funding organisations or institutional boundaries, a decision support system provides information on the next steps and available tools. Alongside, matching trainings for the current step are provided. Furthermore, Jarves offers a broad connectivity to other services, allowing for seamless (meta)data exchange.
Organising & Processing · Publishing & Archiving · Storing & Computing · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
Kadi4Mat is a generic and open source virtual research environment, which can be hosted as a web-based service. The instances hosted at KIT can be leveraged to enhance (meta)data management and integration in the engineering community working in academia, research institutions, or industry.
Organising & Processing · Publishing & Archiving · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
The software ecosystem of Kadi4Mat includes different tools and libraries that are built around and on top of Kadi4Mat, the generic and open source virtual research environment.
Organising & Processing · Publishing & Archiving · Storing & Computing · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
Are you an engineer in a project to (re-)program scientific code? Or are you a student in a likewise project? Or maybe you are a project/data manager looking for some inspiration and advice? Then this Knowledge Base might be just for you! We cover multiple topics regarding the development of scientific software, e.g. Version Control and Continuous Integration.
Storing & Computing · Finding & Re-Using
Are you an engineer in a project to (re-)program scientific code? Or are you a student in a likewise project? Or maybe you are a project/data manager looking for some inspiration and advice? Then this Knowledge Base might be just for you! We cover multiple topics regarding the development of scientific software, e.g. Version Control and Continuous Integration.
Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
The NFDI4ING Metadata Profile Service facilitates creation and utilization of FAIR (RDF-based) metadata by making use of metadata profiles that combine terms from existing ontologies into reusable metadata templates. The platform provides functionality for creation, sharing and curation of metadata profiles.
Storing & Computing · Finding & Re-Using
The MetadataHub enables easy access to multiple repositories via a uniform interface. Metadata documents can be created, updated, read, deleted, listed and searched for. Currently AIMS, Coscine and MetaStore are supported via their REST interfaces. New repositories could be easily added by adding a specific mapping to the MetadataHub service.
Informing & Planning · Publishing & Archiving · Finding & Re-Using
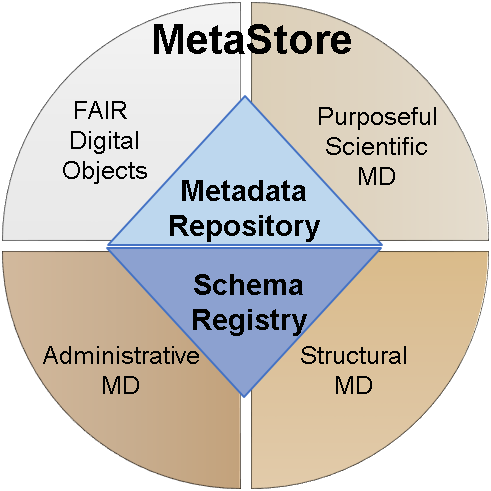
MetaStore is a research data repository for storing metadata documents and schemas for researchers. Quality and consistency are ensured by associating and validating each (metadata) document against a schema registered in beforehand in the MetaStore. XML and JSON are supported as possible schemas.
Publishing & Archiving · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using · Learning & Teaching
The NFDI-RFC (Request For Comments) process is adopted from the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard. This process ensures that NFDI community submitted standards are practical, effective, and widely used within the research community. A review process for the publication of NFDI-RFCs was also designed to ensure that they meet the highest quality and integrity standards.
Learning & Teaching
The NFDI4ING Education Platform provides essential resources for self-paced trainings in RDM tailored specifically to engineering disciplines. Driven by the needs and characteristics of the engineering domain, these trainings provide basic RDM topics adapted for engineering, including use cases and interactive quiz elements. Based on that, users can start learning and enhancing their skills in managing research data effectively, improving collaboration in their projects, and reuse research data.
Storing & Computing · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using · Learning & Teaching
The NFDI4Ing Jupyter Service provides Jupyterlab servers to the NFDI4Ing community. Jupyter allows interactive programming via the browser in more than 40 programming languages. Via computational notebooks, the code can be enriched with text descriptions, images, videos and more (literate programming).
Informing & Planning · Organising & Processing
To evaluate the implementation of research data management, maturity models are provided for individual phases, which researchers can use for self-evaluation. The models are aimed at a standardised and optimised implementation of RDM in engineering research projects.
Informing & Planning · Describing & Documenting · Learning & Teaching
The NFDI4ING Q&A platform is here to empower researchers in the engineering sciences with a collaborative space to ask and answer questions about their research data management. Whether you’re a seasoned expert or just starting out, this platform is designed to foster knowledge exchange and support your research journey.
Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
The NFDI4ING Terminology Service bundles and standardises access to existing terminologies and semantic models for research data management purposes. They form the basis for clear and meaningful communication between producers and users of research data for their subsequent use in innovative research. Clear communication is a basic prerequisite for innovative research, especially in areas such as the highly complex engineering sciences.
Informing & Planning · Organising & Processing · Publishing & Archiving · Storing & Computing · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
The Open Research Knowledge Graph (ORKG) helps researchers find, compare, and reuse scientific findings efficiently. User can organize research contributions semantically so that both humans and machines can easily understand and use them. With ORKG, you can explore knowledge across various disciplines, stay updated, and collaborate on new research. Additionally, ORKG enhances the visibility of research outputs, facilitating better discovery and innovation in the scientific community.
Informing & Planning · Describing & Documenting · Learning & Teaching
The Research Data Management Organiser (RDMO) guides researchers through the planning, implementation and administration of all research data management tasks. It offers structured questionnaires with detailed guidance, enabling efficient and comprehensive data management planning for research projects, ensuring compliance with funding requirements.
Publishing & Archiving · Describing & Documenting · Finding & Re-Using
Ellen's RESODATE will be a service that enables the task- and problem-oriented search and discovery of research data artifacts. Based on formalized procedural information embedded in knowledge graphs, it utilizes relationships between research tasks and methods to organize research software and data according to their possible uses. It aims to support the integration of software and data into executable research workflows that can be used to cover individual information and data requirements.
Organising & Processing · Describing & Documenting
SciKGTeX is a LaTeX package that allows researchers to annotate specific research contributions in their scientific documents. By embedding these annotations into the PDF metadata, SciKGTeX makes it easier for search engines and knowledge graphs to find and understand the research. This enhances the discoverability and usability of scientific work, making it a valuable tool for anyone looking to improve the visibility and impact of their research.
Organising & Processing · Publishing & Archiving · Describing & Documenting
SciMesh provides a specification and a reference implementation for a knowledge graph schema. It is supposed to represent scientific workflows and insights. While originating in experimental research of the engineering and material sciences, its basic principle is the connection of cause and effect, which can be applied to most empiric research. Its applications range from research publication over data exchange between electronic lab notebooks to timestamping of scientific work in blockchains.
Publishing & Archiving
SM4RO-C is a specification that defines how to use SciMesh graphs in RO-Crates in order to describe the raw data files stored within the crate. It enables researchers to publish and/or share their research results in the richest way possible, i.e. raw data, intermediate data, and workflow graphs combined in one ZIP file.